Here I’ll teach you how to manage users, groups and change permissions onfiles and directories in Linux.
Permissions
All files in linux have three permissions: Read, Write and Execute.
You can modify then with chmod command.
For example, we add read and write permission but forbid execution:
sudo chmod 770 file.txtOr:
sudo chmod +rw-x file.txtAnother example, we add read/write to the owner but delete all permissions for the rest of users.
chmod u=rw,go= arch.txt
Managing users and groups
In all machines, we should create an user to manage the system.
Best way to create users and groups, Recommended:
Create/Delete new group:
sudo addgroup jclustergroup sudo delgroup jclustergroupAdd/Delete user to a specific group or system (empty):
sudo adduser juser [jclustergroup/empty] sudo deluser juser [jclustergroup/empty]Add/Change password to user:
sudo passwd juser
We can use lower/upper case in names, Not recommended:
Create/Delete new group:
sudo groupadd JClusterGroup sudo groupdel JClusterGroupCreate/Delete new user:
sudo useradd Juser sudo userdel JuserCreate new user with a group named
JClusterGroupwith home/home/juserand with CLI/bin/bashsudo useradd -g JClusterGroup -d /home/Juser -m -s /bin/bash JuserChange users permissions:
sudo chown -R <username> <files>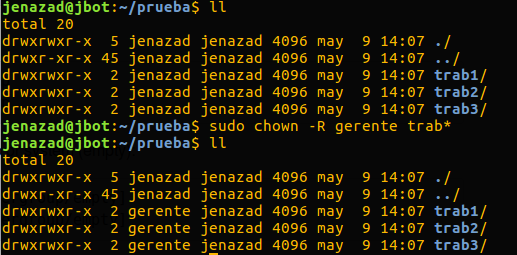
Change groups permisions:
sudo chgrp -R <groupname> <files>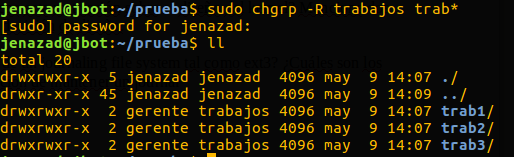
Change actions permissions:
sudo chmod ugo-rw+x <filename>We add execution permission without read/write permission.
