Here you’ll learn to use Virt-Manager to manage your Virtual Machines.
Virt-Manager
Is a desktop-driven virtual machine manager with which users can manage virtual machines (VMs).
Virt-Manager is a Light virtualizer using KVM, Xen and Qemu.
Installing
First, we shoul know how many CPUs can support hardware virtualization:
grep --color -e -svm -e vmx /proc/cpuinfo egrep -c '(svm|vmx)' /proc/cpuinfoThen, installing virt-manager, qemu and kvm:
sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin virtinst kvm virt-manager virt-viewerAdd our principal user to the libvirtd group:
sudo adduser jenazad libvirtdCreate a directory (pool) where you can store the images of each OS (vol):
mkdir /home/$USER/.virtManager/imagesInitializing the virtual manager:
virt-managerShows a list of all guest OS:
virsh -c qemu:///system list --allConnect to VM:
virt-viewer -c qemu:///system vmname
Storage pool
A pool store the information of a group of OS (image).
Create/Define a pool:
virsh pool-create-as --name stgname --type dir --target "/home/$USER/.virtManager/images" virsh pool-define-as --name stgname --type dir --target "/home/$USER/.virtManager/images"Edit a pool:
virsh pool-edit --pool stgnameList all pools:
virsh pool-list --allInitializing pool:
virsh pool-start stgname virsh pool-autostart stgnameDelete/Undefined pool:
If pool was defined, only write destroy, if not, write all this commands:
virsh pool-destroy stgname virsh pool-delete stgname virsh pool-undefine stgname
Virtual Networks
Edit the virtual network:
virsh net-edit netnameList all virtual networks:
virsh net-list --all
Storage Volumen
A vol is the image installed of a OS.
List all vols in a pool:
virsh vol-list --pool stgnameCreate vol:
virsh vol-create-as --pool stgVirt --name volname.qcow2 --capacity 20G --format qcow2Delete vol:
virsh vol-delete --pool stgname volname.qcow2
Virtual Machines
A virtual machine is a guest OS on another OS (host), you can see the xml configuration files on /etc/libvirt/qemu/
Create a VM:
From local iso (example installing Deepin 15.3):
virt-install \ --connect qemu:///system \ --name Deepin15.3_VM \ --memory 2048 \ --vcpus 1 \ --network network=virtualnetworkNAT,model=virtio \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant generic \ --disk path=/home/$USER/VirtStg/images/deepin15.qcow2,size=20 \ --cdrom /home/$USER/Documents/deepin-15.3-amd64.iso \ --graphics spice \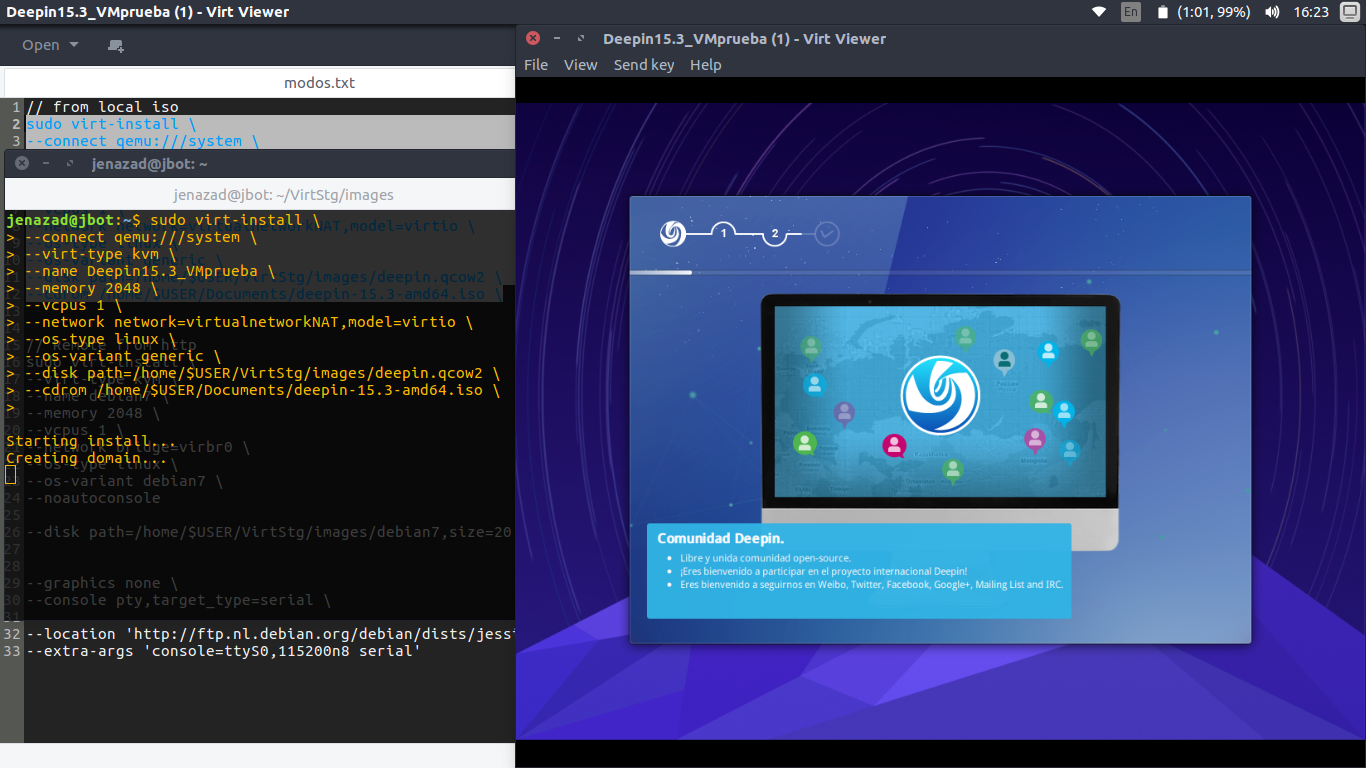
From remote
http/ftpserver (example insalling Debian 8.0):virt-install \ --connect qemu:///system \ --name Debian8.7_VM \ --memory 2048 \ --vcpus 1 \ --network network=virtualnetworkNAT,model=virtio \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant generic \ --disk path=/home/$USER/VirtStg/images/debian8.qcow2,size=20 \ --location 'http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/jessie/main/installer-amd64/' \ --graphics none \ --console pty,target_type=serial \ --extra-args 'console=ttyS0,115200n8 serial'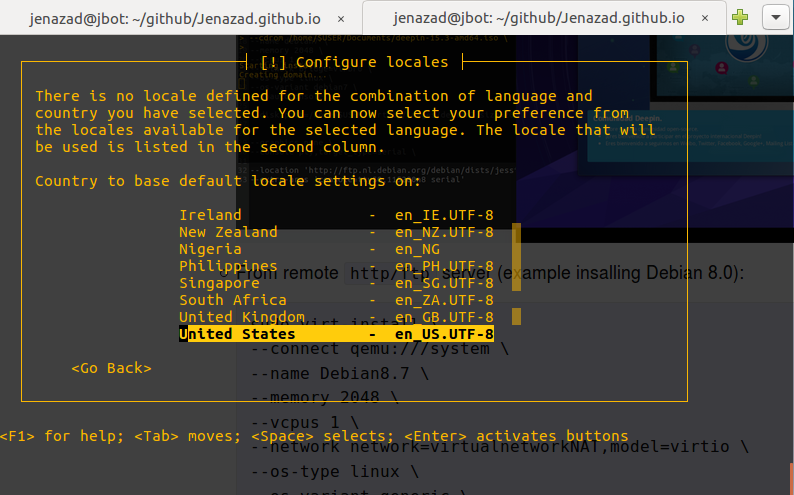
From remote
http/ftpserver (another example Fedora 26):virt-install \ --connect qemu:///system \ --name Fedora26_VM \ --memory 2048 \ --vcpus 1 \ --network network=virtualnetworkNAT,model=virtio \ --os-type linux \ --os-variant generic \ --disk path=/home/$USER/VirtStg/images/fedora26.qcow2,size=20 \ --location 'http://mirror.globo.com/fedora/linux/releases/25/Workstation/x86_64/os' \ --graphics spice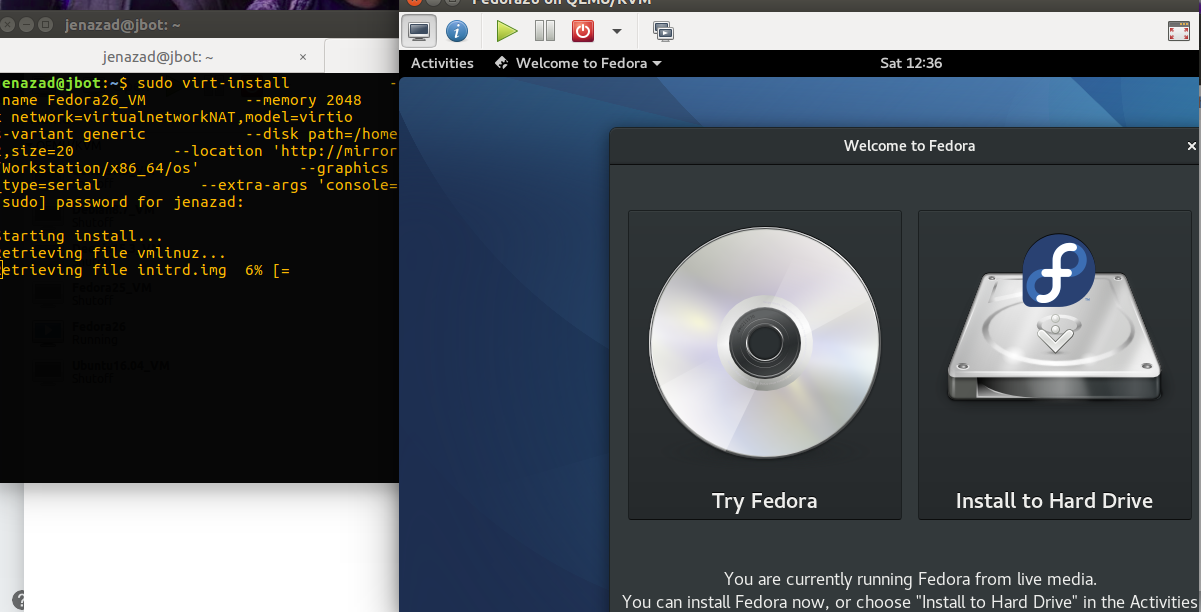
Delete a VM:
virsh destroy vmname virsh undefine vmnameList all VM:
virsh list --allStart/reboot/shutdown VM:
virsh start vmname virsh reboot vmname virsh shutdown vmnameSave/restore state of a VM:
virsh save vmname vmname-20170318.state virsh restore vmname-20170318.stateClone a VM:
virt-clone --connect=qemu:///system -o originalvm -n copyvm -f /path/to/copyvm.qcow2Create VM using virt-manager interface:
step 1: Choose the method to install.
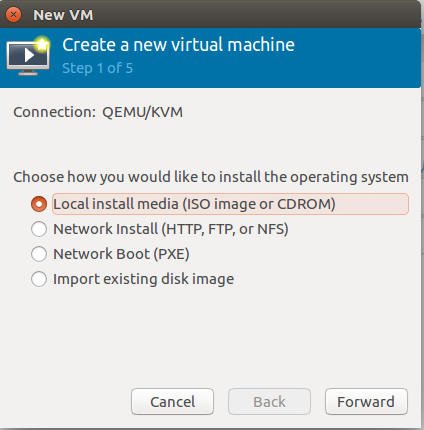
step 2: Select the ISO image.
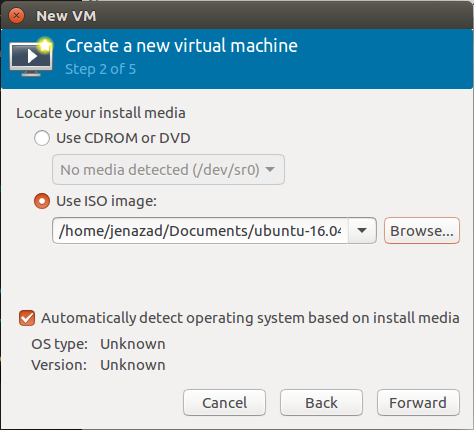
step 3: Set RAM memory.
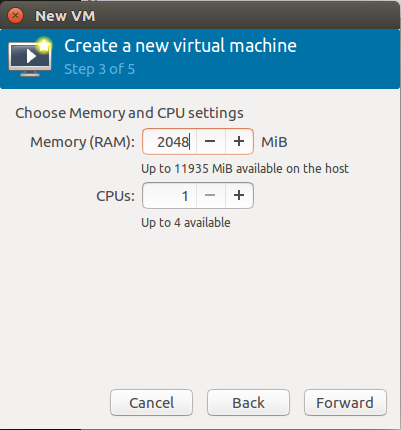
step 4: Create/Set a disk storage for the file system of the guest OS.
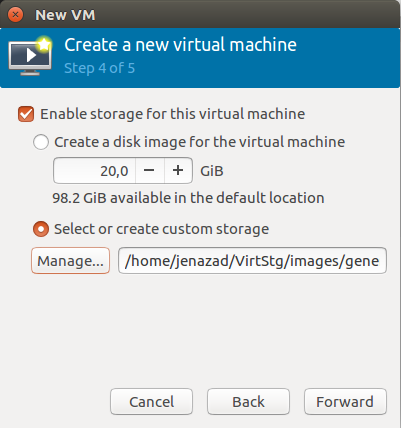
step 5: Write the OS name, select the network and choose (optional) more configurations.
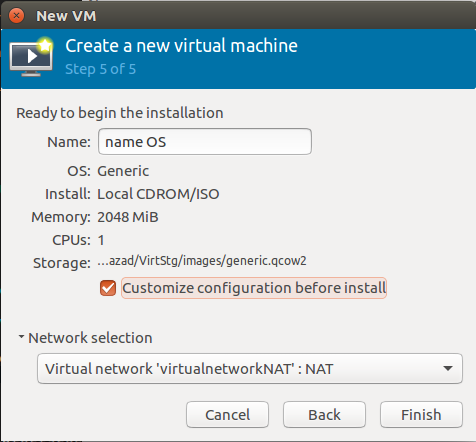
step 6 (optional): Advanced configurations.
To configureyour VM depending of your OS, press here.
